Ammonium sulfate
| Ammonium sulfate | |
|---|---|
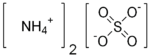 |
|
|
Ammonium sulfate
|
|
|
Other names
ammonium sulfate (2:1)
diammonium sulfate sulfuric acid diammonium salt mascagnite Actamaster Dolamin |
|
| Identifiers | |
| CAS number | 7783-20-2 |
| ChemSpider | 22944 |
|
SMILES
O=S(=O)(O)O.N.N
|
|
|
InChI
InChI=1/2H3N.H2O4S/c;;1-5(2,3)4/h2*1H3;(H2,1,2,3,4)
Key: BFNBIHQBYMNNAN-UHFFFAOYAI |
|
| Properties | |
| Molecular formula | (NH4)2SO4 |
| Molar mass | 132.14 g/mol |
| Appearance | Fine white hygroscopic granules or crystals. |
| Density | 1.769 g/cm3 (20 °C) |
| Melting point |
235-280 °C, 508-553 K, 455-536 °F (decomposes) |
| Solubility in water | 70.6 g/100 mL (0 °C) 74.4 g/100 mL (20 °C) 103.8 g/100 mL (100 °C)[1] |
| Solubility | insoluble in acetone, alcohol and ether |
| Critical relative humidity | 79.2% (30 °C) |
| Hazards | |
| EU Index | Not listed |
| NFPA 704 |
 1
2
0
|
| Flash point | Non-flammable |
| LD50 | 2840 mg/kg, rat (oral) |
| Related compounds | |
| Other anions | Ammonium thiosulfate Ammonium sulfite Ammonium bisulfate Ammonium persulfate |
| Other cations | Sodium sulfate Potassium sulfate |
| Related compounds | Ammonium iron(II) sulfate |
| Except where noted otherwise, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C, 100 kPa) |
|
| Infobox references | |
Ammonium sulfate (IUPAC-recommended spelling; also ammonium sulphate in British English), (NH4)2SO4, is an inorganic salt with a number of commercial uses. The most common use is as a soil fertilizer. It contains 21% nitrogen as ammonium cations, and 24% sulfur as sulfate anions. In fertilizer the purpose of the sulfate is to reduce the soil pH.
Contents |
Uses
It is used largely as an artificial fertilizer for alkaline soils. In the soil the sulfate ion is released and forms bisulfate, lowering the pH balance of the soil (as do other sulfate compounds such as aluminium sulfate), while contributing essential nitrogen for plant growth.
It is also used as an agricultural spray adjuvant for water soluble insecticides, herbicides, and fungicides. There it functions to bind iron and calcium cations that are present in both well water and plant cells. It is particularly effective as an adjuvant for 2,4-D (amine), glyphosate, and glufosinate herbicides.
It is also used in the preparation of other ammonium salts.
In biochemistry, ammonium sulfate precipitation is a common method for purifying proteins by precipitation. As such, ammonium sulfate is also listed as an ingredient for many United States vaccines per the Center for Disease Control.[2]
Ammonium sulfate is also a food additive.[3][4]
A saturated solution of ammonium sulfate in heavy water (D2O) is used as an external standard in sulfur (33S) NMR spectroscopy with shift value of 0 ppm.
It has also been used in flame retardant compositions acting much like Diammonium phosphate. As a flame retardant, it lowers the combustion temperature of the material, decreases maximum weight loss rates, and causes an increase in the production of residue or char.[5]
In November 2009, a ban on ammonium sulfate, ammonium nitrate and calcium ammonium nitrate fertilizers was imposed in the Malakand Division - comprising the Dir, Swat, Chitral and Malakand districts of the North West Frontier Province (NWFP) of Pakistan, by the NWFP government, following reports that those chemicals were used by militants to make explosives. In January 2010, these substances were also banned in Afghanistan for the same reason.
Preparation
Ammonium sulfate is made by reacting synthetic ammonia (or by-product ammonia from coke-ovens) with sulfuric acid:[6]
- 2 NH3 + H2SO4 → (NH4)2SO4
A mixture of ammonia gas and water vapor is introduced into a reactor that contains a saturated solution of ammonium sulfate and about 2 to 4% of free sulfuric acid at 60 °C. Concentrated sulfuric acid is added to keep the solution acidic, and to retain its level of free acid. The heat of reaction keeps reactor temperature at 60 °C.
Dry, powdered ammonium sulfate may be formed by spraying sulfuric acid into a reaction chamber filled with ammonia gas. The heat of reaction evaporates all water present in the system, forming a powdery salt.
Ammonium sulfate also is manufactured from gypsum (CaSO4·2H2O). Finely divided gypsum is added to an ammonium carbonate solution. Calcium carbonate precipitates out, leaving ammonium sulfate in the solution.
- (NH4)2CO3 + CaSO4 → (NH4)2SO4 + CaCO3
Ammonium sulfate occurs naturally as the rare mineral mascagnite in volcanic fumaroles and due to coal fires on some dumps.[7]
Reactions
Ammonium sulfate decomposes upon heating at 100 °C in an open system, forming ammonium bisulfate. As a salt of a strong acid (i.e. H2SO4) and weak base (i.e. NH3), its solution is acidic; pH of 0.1M solution is 5.5.
In aqueous solution the reactions are those of NH4+ and SO4−2 ions. For example, addition of barium chloride, precipitates out barium sulfate. The filtrate on evaporation yields ammonium chloride.
Ammonium sulfate forms many double salts (ammonium metal sulfates) when its solution is mixed with equimolar solutions of metal sulfates and the solution is slowly evaporated. Such double metal sulfates include ammonium cobaltous sulfate, ferric ammonium sulfate, ammonium nickel sulfate and ammonium cerous sulfate. [6]
References
- ↑ Handbook of Chemistry and Physics
- ↑ Pink Book | Appendix B: Vaccine Excipient & Media Summary, Part 2
- ↑ Panera Bread › Menu & Nutrition › Nutrition Information Profile
- ↑ Official Subway Restaurants U.S. Products Ingredients Guide
- ↑ George, C.W.; Susott, R.A. (April 1971), "Effects of Ammonium Phosphate and Sulfate on the Pyrolysis and Combustion of Cellulose", Research Paper INT-90 (Intermountain Forest and Range Experiment Station: USDA Forest Service), http://openlibrary.org/b/OL16022833M/Effects_of_ammonium_phosphate_and_sulfate_on_the_pyrolysis_and_combustion_of_cellulose
- ↑ 6.0 6.1 Pradyot Patnaik. Handbook of Inorganic Chemicals. McGraw-Hill, 2002, ISBN 0070494398
- ↑ http://www.mindat.org/min-2584.html/ Mindat data
Further reading
- Properties: UNIDO and International Fertilizer Development Center (1998), Fertilizer Manual, Kluwer Academic Publishers, ISBN 0-7923-5032-4.